Gophercon 2018 - Computer Vision Using Go and OpenCV 3
Presenter: Ron Evans
Liveblogger: @beyang
Summary
An introduction to and tour of computer vision programs written in Go using GoCV––with code snippets and live demos!
Ron Evans is the creator of open source robotics projects Gobot.io and Gocv.io, and the leader of The Hybrid Group, the "software company that makes hardware companies look good."

What is computer vision?
Computer vision applications include
- Motion detection
- People recognition
- Telepresence
- Autonomous vehicles
- Augmented humans (e.g., IoT, tech-enhanced surgery)
Why should you use Go for computer vision? Well, the same reasons you should use Go for everything!
- Concurrency
- Portability
- Performance
How GoCV works
GO → CGO → C → C++

That sounds complex, but they've done all the hard work for you, so you just have to write Go.
Works on Linux, macOS, and even Windows.
The "Hello, World" of video
package main
import (
"gocv.io/x/gocv"
)
func main() {
webcam, _ := gocv.VideoCaptureDevice(0)
window := gocv.NewWindow("Hello")
img := gocv.NewMat()
for {
webcam.Read(&img)
window.IMShow(img)
gocv.WaitKey(1)
}
}Demo! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nyk-gWpqJ8A
Into the Mat(rix)
The fundamental unit of data you manipulate in OpenCV is the Mat (short for "matrix").

A grayscale image is a Mat with 2 dimensions, each value is a 16-bit integer (representing the intensity of the pixel).

An RGB color image has 2 dimensions, each value is a 16-bit integer, but 3 channels (one for red, green, and blue).

A Mat can also represent other types of data, like a 3D point cloud:

4 applications using GoCV
Lets take a look at 4 tiny applications that represent the typical applications you might want to solve in computer vision.
Application 1: Face tracking
Well, face tracking isn't cool anymore. There are privacy concerns. So let's talk about face blurring instead :)
Haar wavelets are useful features for face detection:

Here's a wavelet that's good for eyes:

Here's one that works well for the nose:

Or, we could just use the gocv CascadeClassifier--easier since we've done the hard stuff for you:
gocv.CascadeClassifier{}package main
import (
"fmt"
"image"
"os"
"strconv"
"gocv.io/x/gocv"
)
func main() {
if len(os.Args) < 3 {
fmt.Println("How to run:\n\tfaceblur [camera ID] [classifier XML file]")
return
}
// parse args
deviceID, _ := strconv.Atoi(os.Args[1])
xmlFile := os.Args[2]
// open webcam
webcam, err := gocv.VideoCaptureDevice(deviceID)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error opening video capture device: %v\n", deviceID)
return
}
defer webcam.Close()
// open display window
window := gocv.NewWindow("Face Blur")
defer window.Close()
// prepare image matrix
img := gocv.NewMat()
defer img.Close()
// load classifier to recognize faces
classifier := gocv.NewCascadeClassifier()
defer classifier.Close()
classifier.Load(xmlFile)
fmt.Printf("start reading camera device: %v\n", deviceID)
for {
if ok := webcam.Read(&img); !ok {
fmt.Printf("cannot read device %d\n", deviceID)
return
}
if img.Empty() {
continue
}
// detect faces
rects := classifier.DetectMultiScale(img)
fmt.Printf("found %d faces\n", len(rects))
// blur each face on the original image
for _, r := range rects {
imgFace := img.Region(r)
// blur face
gocv.GaussianBlur(imgFace, &imgFace, image.Pt(75, 75), 0, 0, gocv.BorderDefault)
imgFace.Close()
}
// show the image in the window, and wait 1 millisecond
window.IMShow(img)
if window.WaitKey(1) >= 0 {
break
}
}
}Demo! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dlP8dSl92jk
Application 2: Motion detection/tracking
- Background subtraction
- Mixture of Gaussian (MoG)
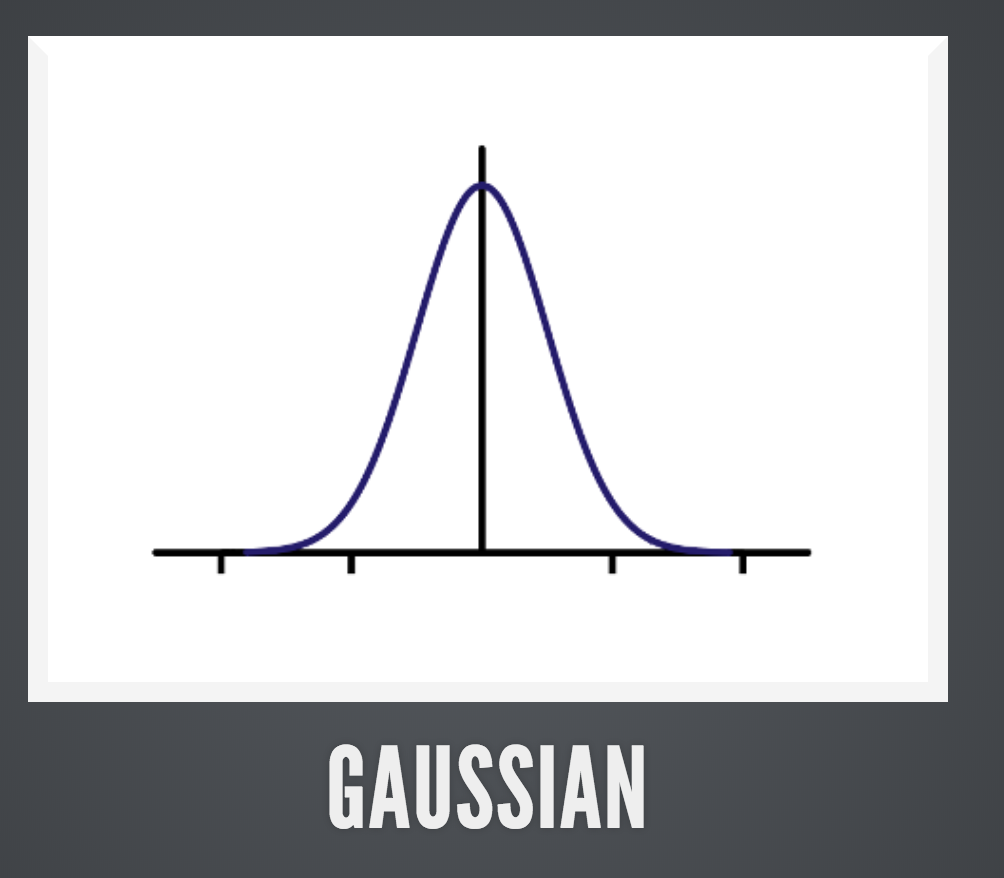


gocv.BackgroundSubtractorMOG2{}package main
import (
"fmt"
"image"
"image/color"
"os"
"strconv"
"gocv.io/x/gocv"
)
const MinimumArea = 3000
func main() {
if len(os.Args) < 2 {
fmt.Println("How to run:\n\tmotion-detect [camera ID]")
return
}
// parse args
deviceID, _ := strconv.Atoi(os.Args[1])
webcam, err := gocv.VideoCaptureDevice(int(deviceID))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error opening video capture device: %v\n", deviceID)
return
}
defer webcam.Close()
window := gocv.NewWindow("Motion Window")
defer window.Close()
img := gocv.NewMat()
defer img.Close()
imgDelta := gocv.NewMat()
defer imgDelta.Close()
imgThresh := gocv.NewMat()
defer imgThresh.Close()
mog2 := gocv.NewBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
defer mog2.Close()
status := "Ready"
fmt.Printf("Start reading camera device: %v\n", deviceID)
for {
if ok := webcam.Read(&img); !ok {
fmt.Printf("Error cannot read device %d\n", deviceID)
return
}
if img.Empty() {
continue
}
status = "Ready"
statusColor := color.RGBA{0, 255, 0, 0}
// first phase of cleaning up image, obtain foreground only
mog2.Apply(img, &imgDelta)
// remaining cleanup of the image to use for finding contours.
// first use threshold
gocv.Threshold(imgDelta, &imgThresh, 25, 255, gocv.ThresholdBinary)
// then dilate
kernel := gocv.GetStructuringElement(gocv.MorphRect, image.Pt(3, 3))
defer kernel.Close()
gocv.Dilate(imgThresh, &imgThresh, kernel)
// now find contours
contours := gocv.FindContours(imgThresh, gocv.RetrievalExternal, gocv.ChainApproxSimple)
for i, c := range contours {
area := gocv.ContourArea(c)
if area < MinimumArea {
continue
}
status = "Motion detected"
statusColor = color.RGBA{255, 0, 0, 0}
gocv.DrawContours(&img, contours, i, statusColor, 2)
rect := gocv.BoundingRect(c)
gocv.Rectangle(&img, rect, color.RGBA{0, 0, 255, 0}, 2)
}
gocv.PutText(&img, status, image.Pt(10, 20), gocv.FontHersheyPlain, 1.2, statusColor, 2)
window.IMShow(img)
if window.WaitKey(1) == 27 {
break
}
}
}Demo! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L5k53lkzECg
Application 3: MJPEG streaming
MJPEG stands for Motion-JPEG. I.e., "how do I get my webcam to livestream on the Internet?"
We're going to use GoCV to take what's in the webcam and stream it on a webpage.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"strconv"
"github.com/hybridgroup/mjpeg"
"gocv.io/x/gocv"
)
var (
deviceID int
err error
webcam *gocv.VideoCapture
stream *mjpeg.Stream
)
func main() {
if len(os.Args) < 3 {
fmt.Println("How to run:\n\tmjpeg-streamer [camera ID] [host:port]")
return
}
// parse args
deviceID, _ = strconv.Atoi(os.Args[1])
host := os.Args[2]
// open webcam
webcam, err = gocv.VideoCaptureDevice(deviceID)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error opening video capture device: %v\n", deviceID)
return
}
defer webcam.Close()
// create the mjpeg stream
stream = mjpeg.NewStream()
// start capturing
go capture()
fmt.Println("Capturing. Point your browser to " + host)
// start http server
http.Handle("/", stream)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(host, nil))
}
func capture() {
img := gocv.NewMat()
defer img.Close()
for {
if ok := webcam.Read(&img); !ok {
fmt.Printf("cannot read device %d\n", deviceID)
return
}
if img.Empty() {
continue
}
buf, _ := gocv.IMEncode(".jpg", img)
stream.UpdateJPEG(buf)
}
}Demo! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Gi9-eOtJRw
Object classification/tracking
Now let's take a look at object classification/tracking with a deep neural net––and a drone. Specifically, the Caffe Deep Learning Framework and the DJI Tello.
A neural network simulates the way a biological synapse works and allows us to solve certain types of machine learning problems that can't be solved with more classical programming methods.
The DJI Tello has an Intel chip that's optimized for performing neural network computations onboard the drone and is only $99.
We'll use the OpenCV face tracking SSD model:
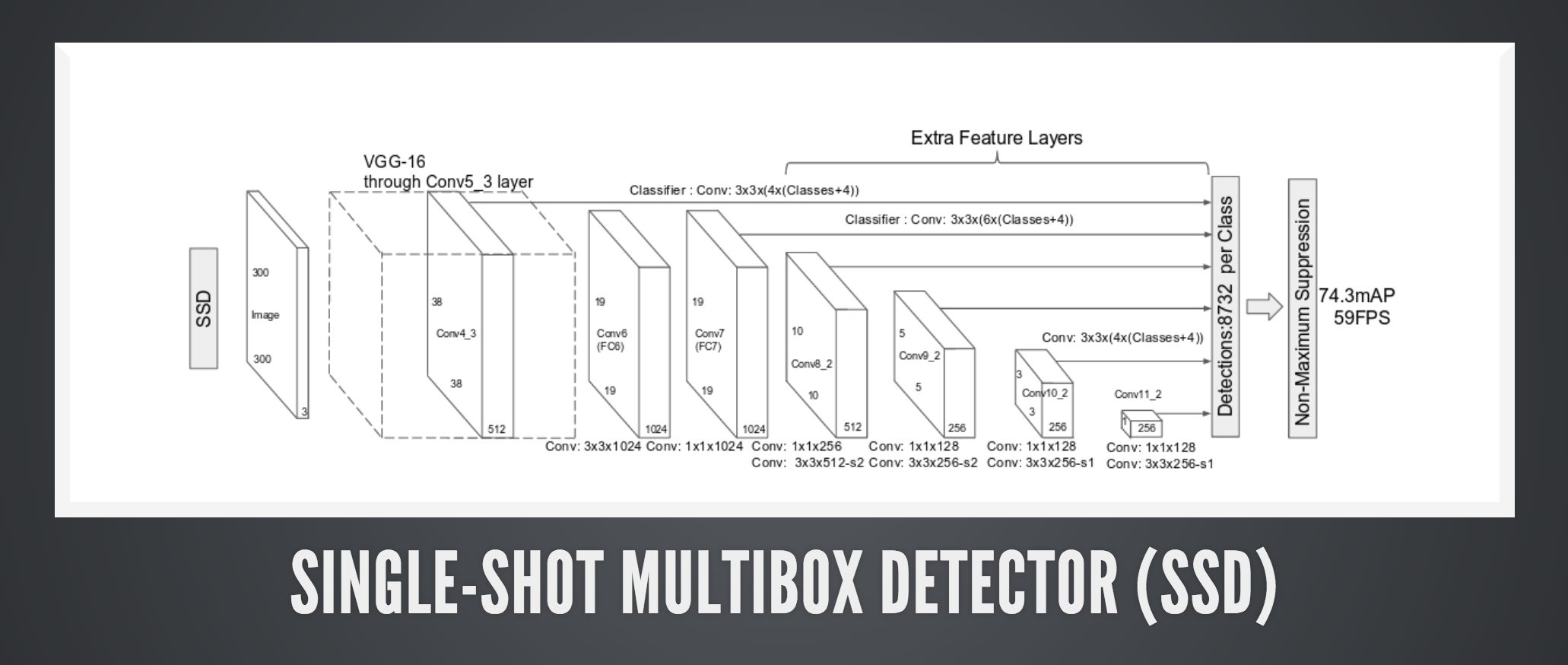
gocv.Net{}package main
import (
"fmt"
"image"
"image/color"
"io"
"math"
"os"
"os/exec"
"strconv"
"sync/atomic"
"time"
"gobot.io/x/gobot"
"gobot.io/x/gobot/platforms/dji/tello"
"gobot.io/x/gobot/platforms/joystick"
"gocv.io/x/gocv"
)
type pair struct {
x float64
y float64
}
const (
frameX = 400
frameY = 300
frameSize = frameX * frameY * 3
offset = 32767.0
)
var (
// ffmpeg command to decode video stream from drone
ffmpeg = exec.Command("ffmpeg", "-hwaccel", "auto", "-hwaccel_device", "opencl", "-i", "pipe:0",
"-pix_fmt", "bgr24", "-s", strconv.Itoa(frameX)+"x"+strconv.Itoa(frameY), "-f", "rawvideo", "pipe:1")
ffmpegIn, _ = ffmpeg.StdinPipe()
ffmpegOut, _ = ffmpeg.StdoutPipe()
// gocv
window = gocv.NewWindow("Tello")
net *gocv.Net
green = color.RGBA{0, 255, 0, 0}
// tracking
tracking = false
detected = false
detectSize = false
distTolerance = 0.05 * dist(0, 0, frameX, frameY)
refDistance float64
left, top, right, bottom float64
// drone
drone = tello.NewDriver("8890")
flightData *tello.FlightData
// joystick
joyAdaptor = joystick.NewAdaptor()
stick = joystick.NewDriver(joyAdaptor, "dualshock4")
leftX, leftY, rightX, rightY atomic.Value
)
func init() {
leftX.Store(float64(0.0))
leftY.Store(float64(0.0))
rightX.Store(float64(0.0))
rightY.Store(float64(0.0))
// process drone events in separate goroutine for concurrency
go func() {
// process joystick events
handleJoystick()
if err := ffmpeg.Start(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
drone.On(tello.FlightDataEvent, func(data interface{}) {
// TODO: protect flight data from race condition
flightData = data.(*tello.FlightData)
})
drone.On(tello.ConnectedEvent, func(data interface{}) {
fmt.Println("Connected")
drone.StartVideo()
drone.SetVideoEncoderRate(tello.VideoBitRateAuto)
drone.SetExposure(0)
gobot.Every(100*time.Millisecond, func() {
drone.StartVideo()
})
})
drone.On(tello.VideoFrameEvent, func(data interface{}) {
pkt := data.([]byte)
if _, err := ffmpegIn.Write(pkt); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
})
robot := gobot.NewRobot("tello",
[]gobot.Connection{joyAdaptor},
[]gobot.Device{drone, stick},
)
robot.Start()
}()
}
func main() {
if len(os.Args) < 5 {
fmt.Println("How to run:\ngo run facetracker.go [model] [config] ([backend] [device])")
return
}
model := os.Args[1]
config := os.Args[2]
backend := gocv.NetBackendDefault
if len(os.Args) > 3 {
backend = gocv.ParseNetBackend(os.Args[3])
}
target := gocv.NetTargetCPU
if len(os.Args) > 4 {
target = gocv.ParseNetTarget(os.Args[4])
}
n := gocv.ReadNet(model, config)
if n.Empty() {
fmt.Printf("Error reading network model from : %v %v\n", model, config)
return
}
net = &n
defer net.Close()
net.SetPreferableBackend(gocv.NetBackendType(backend))
net.SetPreferableTarget(gocv.NetTargetType(target))
for {
// get next frame from stream
buf := make([]byte, frameSize)
if _, err := io.ReadFull(ffmpegOut, buf); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
continue
}
img, _ := gocv.NewMatFromBytes(frameY, frameX, gocv.MatTypeCV8UC3, buf)
if img.Empty() {
continue
}
trackFace(&img)
window.IMShow(img)
if window.WaitKey(10) >= 0 {
break
}
}
}
func trackFace(frame *gocv.Mat) {
W := float64(frame.Cols())
H := float64(frame.Rows())
blob := gocv.BlobFromImage(*frame, 1.0, image.Pt(300, 300), gocv.NewScalar(104, 177, 123, 0), false, false)
defer blob.Close()
net.SetInput(blob, "data")
detBlob := net.Forward("detection_out")
defer detBlob.Close()
detections := gocv.GetBlobChannel(detBlob, 0, 0)
defer detections.Close()
for r := 0; r < detections.Rows(); r++ {
confidence := detections.GetFloatAt(r, 2)
if confidence < 0.5 {
continue
}
left = float64(detections.GetFloatAt(r, 3)) * W
top = float64(detections.GetFloatAt(r, 4)) * H
right = float64(detections.GetFloatAt(r, 5)) * W
bottom = float64(detections.GetFloatAt(r, 6)) * H
left = math.Min(math.Max(0.0, left), W-1.0)
right = math.Min(math.Max(0.0, right), W-1.0)
bottom = math.Min(math.Max(0.0, bottom), H-1.0)
top = math.Min(math.Max(0.0, top), H-1.0)
detected = true
rect := image.Rect(int(left), int(top), int(right), int(bottom))
gocv.Rectangle(frame, rect, green, 3)
}
if !tracking || !detected {
return
}
if detectSize {
detectSize = false
refDistance = dist(left, top, right, bottom)
}
distance := dist(left, top, right, bottom)
// x axis
switch {
case right < W/2:
drone.CounterClockwise(50)
case left > W/2:
drone.Clockwise(50)
default:
drone.Clockwise(0)
}
// y axis
switch {
case top < H/10:
drone.Up(25)
case bottom > H-H/10:
drone.Down(25)
default:
drone.Up(0)
}
// z axis
switch {
case distance < refDistance-distTolerance:
drone.Forward(20)
case distance > refDistance+distTolerance:
drone.Backward(20)
default:
drone.Forward(0)
}
}
func dist(x1, y1, x2, y2 float64) float64 {
return math.Sqrt((x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1))
}
func handleJoystick() {
stick.On(joystick.CirclePress, func(data interface{}) {
drone.Forward(0)
drone.Up(0)
drone.Clockwise(0)
tracking = !tracking
if tracking {
detectSize = true
println("tracking")
} else {
detectSize = false
println("not tracking")
}
})
stick.On(joystick.SquarePress, func(data interface{}) {
fmt.Println("battery:", flightData.BatteryPercentage)
})
stick.On(joystick.TrianglePress, func(data interface{}) {
drone.ThrowTakeOff()
println("Takeoff")
})
stick.On(joystick.XPress, func(data interface{}) {
drone.PalmLand()
println("Land")
})
stick.On(joystick.LeftX, func(data interface{}) {
val := float64(data.(int16))
leftX.Store(val)
})
stick.On(joystick.LeftY, func(data interface{}) {
val := float64(data.(int16))
leftY.Store(val)
})
stick.On(joystick.RightX, func(data interface{}) {
val := float64(data.(int16))
rightX.Store(val)
})
stick.On(joystick.RightY, func(data interface{}) {
val := float64(data.(int16))
rightY.Store(val)
})
gobot.Every(50*time.Millisecond, func() {
rightStick := getRightStick()
switch {
case rightStick.y < -10:
drone.Forward(tello.ValidatePitch(rightStick.y, offset))
case rightStick.y > 10:
drone.Backward(tello.ValidatePitch(rightStick.y, offset))
default:
drone.Forward(0)
}
switch {
case rightStick.x > 10:
drone.Right(tello.ValidatePitch(rightStick.x, offset))
case rightStick.x < -10:
drone.Left(tello.ValidatePitch(rightStick.x, offset))
default:
drone.Right(0)
}
})
gobot.Every(50*time.Millisecond, func() {
leftStick := getLeftStick()
switch {
case leftStick.y < -10:
drone.Up(tello.ValidatePitch(leftStick.y, offset))
case leftStick.y > 10:
drone.Down(tello.ValidatePitch(leftStick.y, offset))
default:
drone.Up(0)
}
switch {
case leftStick.x > 20:
drone.Clockwise(tello.ValidatePitch(leftStick.x, offset))
case leftStick.x < -20:
drone.CounterClockwise(tello.ValidatePitch(leftStick.x, offset))
default:
drone.Clockwise(0)
}
})
}
func getLeftStick() pair {
s := pair{x: 0, y: 0}
s.x = leftX.Load().(float64)
s.y = leftY.Load().(float64)
return s
}
func getRightStick() pair {
s := pair{x: 0, y: 0}
s.x = rightX.Load().(float64)
s.y = rightY.Load().(float64)
return s
}Demo! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XnMoUCby1v0
Wrap-up
Check out GoCV.io or follow the Twitter account @GoCVio!
About the author
Beyang Liu is the CTO and co-founder of Sourcegraph. Beyang studied Computer Science at Stanford, where he published research in probabilistic graphical models and computer vision at the Stanford AI Lab. You can chat with Beyang on Twitter @beyang or our community Discord.